CompTIA A+ course validates your skills in installing, maintaining, troubleshooting, and securing computer hardware and software across various platforms. Edoxi Training Institute offers comprehensive training for the CompTIA A+ certification in Dubai. As an official CompTIA delivery partner and KHDA-approved training center, Edoxi is committed to providing high-quality CompTIA Training in Dubai. Our 40-hour CompTIA A+ Training aims to equip you with essential skills in hardware, software, networking, and security fundamentals.
The CompTIA A+ Course offers you a clear path to breaking into the IT industry through an entry-level role like IT support and administration roles. The CompTIA A+ course includes hands-on labs on hardware troubleshooting, PC assembling, operating system installations, and network configurations. The CompTIA A+ training aligns with the latest CompTIA A+ Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) exam objectives. This ensures that you gain the technical expertise required for key industries in Dubai, including finance, healthcare, retail, hospitality, government, and education.
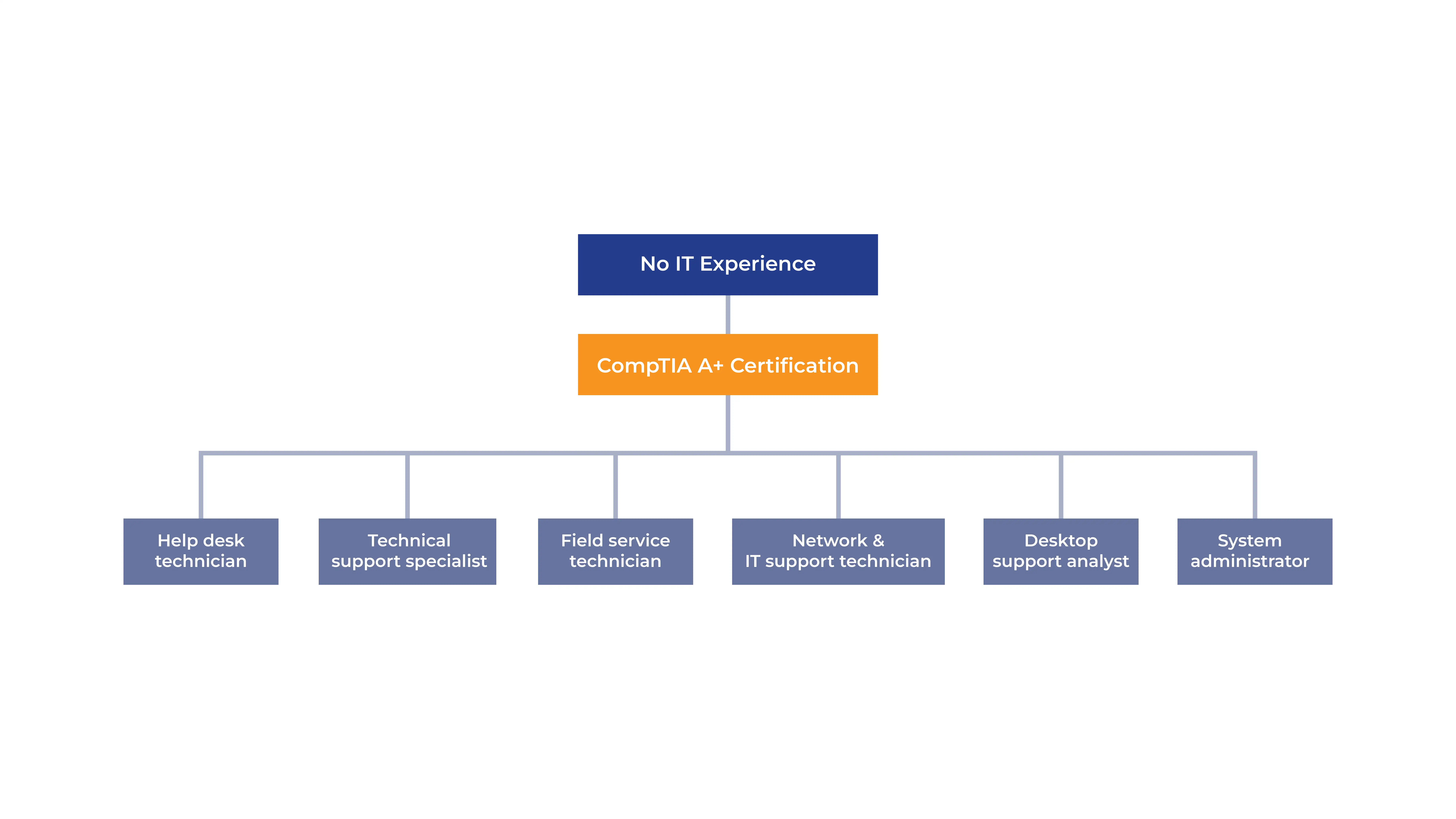
Edoxi’s CompTIA A+ Certification course will fully equip you with the skills to successfully ace the new CompTIA A+ 220-1201/1202 certification exam. After completing Edoxi’s CompTIA A+ Certification course in Dubai, you will open doors to exciting career opportunities, from help desk support to cybersecurity. You can also choose pathways to advance your career through specialised certifications like Network+ or Security+.
CompTIA A+ is a vendor-neutral certification and is ideal for aspiring IT professionals, fresh graduates, and career changers. It requires no prior IT experience and is accessible to anyone with basic computer literacy and a passion for technology.
CompTIA A+ Certification Exam Details
The following table showcases everything about CompTIA A+ Certification exam.
| Exam Criteria | Details |
| Exam Code | Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) |
| Exam Duration | 90 minutes per exam |
| Number of Questions | 90 questions per exam |
| Question Types | Multiple-choice, drag-and-drop, performance-based |
| Passing Score | Core 1: 675/900, Core 2: 700/900 |
|
Exam Fees
|
USD 253 + Taxes per exam
|
|
Certification Validity
|
3 years
|
|
Exam Administration
|
Pearson VUE (online with proctoring or in-person)
|
You get to experience hands-on hardware training by building and troubleshooting complete computer systems using professional diagnostic tools and BIOS utilities.
You will practice step-by-step installation and configuration of Windows operating systems, with basic coverage of Linux and macOS environments.
You will configure and test network settings using essential tools like ipconfig while learning the proper implementation of routers, switches, and firewalls.
You will apply systematic troubleshooting methodologies through real-world scenarios covering hardware, software, and network issues as outlined in Core 1 Domain 5.
You will learn to implement and configure essential security tools, including antivirus software, firewalls, and encryption protocols.
You will get access to detailed PDF study materials covering all exam objectives for both Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) certifications.
Individuals looking to start their career in IT support and administration.
Recent graduates seeking to build a foundation in IT infrastructure and support.
Professionals from various backgrounds wanting to move into IT roles.
Current helpdesk technicians and support specialists aiming to advance their careers.
Individuals with a passion for technology looking to gain knowledge in hardware, software, and networking.
Professionals planning to pursue advanced CompTIA certifications like Network+ or Security+.
The CompTIA A+ certification opens doors to diverse IT career opportunities across Dubai's technology sector. This certification serves as a proven foundation for progression from entry-level positions to specialized technical roles. Here are few training outcomes that you can expect from our CompTIA A+ Course in Dubai;

Get expert assistance in getting your CompTIA A+ Course customised!
Here’s a four-step guide to becoming a certified CompTIA A+ professional.
Join Edoxi’s CompTIA A+ Course
Here are a few reasons why you should choose Edoxi for CompTIA A+ training in Dubai;
Edoxi is an authorised CompTIA training partner, offering a KHDA-approved curriculum aligned with the latest Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) exam objectives.
We offer hands-on experience in hardware labs, including PC assembly, network configuration, and real-world troubleshooting.
Our industry-led trainer will guide you through a structured learning path, providing study materials and resources for both beginners and those changing careers.
We offer flexible training options, including classroom, online, and corporate formats, with a 40-hour adaptable curriculum.
Our trainers are certified IT professionals with expertise in hardware troubleshooting, network configuration, and security.

Our mentors are leaders and experts in their fields. They can challenge and guide you on your road to success!

Sid Ahmed
Sid Ahmed is an IT network infrastructure and security trainer with over 12 years of experience at Edoxi Training Institute, Dubai. He is a certified CCNA/CCNP instructor and NSE 4 trainer and possesses advanced expertise in Cisco networking His portfolio includes prestigious Cisco certifications and hands-on knowledge of global security frameworks, making him a leader in delivering industry-relevant training.
Sid’s knowledge also extends to industry standards such as ISO 27001, NIST, SOC2, and PCI DSS, further strengthening his cybersecurity prowess.Sid Ahmed focuses on developing practical skills through hands-on training with enterprise-grade equipment. As an experienced Network and Security Architect, Sid Ahmed's expertise spans WAN/LAN, IP-MPLS, BGP, Wireless, IP Telephony, and Cybersecurity.He is skilled in HLD/LLD design, audits, pentesting, IT risk assessments, and security frameworks His specialisations include SD-WAN, VPN, VLAN, SSL, SIEM, cloud tech, and routing protocols (OSPF, BGP, STP) Sid is also proficient in Python, MySQL, JavaScript, APIs, and tools like SolarWinds, FortiSIEM, and U2000.
Here is the list of other major locations where Edoxi offers CompTIA A+ Certification Course